Enter your address to receive notifications about new posts to your email.
Articles by Marisa Wexler (43 results)
-
Mixed up: Insights into artificial sequencing chimeras
Sequencing a genome is not as simple as reading a book. All those neatly lined up letters are the final product of a complex process made up of many intricate steps that can—and do—go wrong. In a report published in G3: Genes|Genomes|Genetics, Peccoud et al. put their painful sequencing experiences to good use providing new insights into…
-
Pointing to problems with textbook arrows
You’ve probably encountered at least one diagram in a biology textbook that didn’t make any sense to you. Although these pictures are supposed to clarify ideas, sometimes they leave readers befuddled. This is a particular problem for students; experts looking at schematics are able to fall back on their knowledge of a subject, while novices…
-
Inside the genome of a deadly desert disease
Rhinocladiella mackenziei is a fungus that infects the human brain. It is the most common cause of neurological fungal infections in arid regions of the Middle East, and it is fatal in 70% of cases. However, little is understood about this lethal pathogen—not even its natural habitat. To learn more about the biology of R.…
-
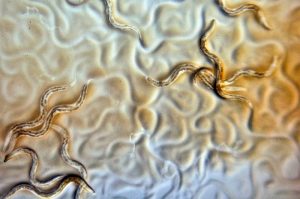
‘Worm’ing through chromosome 21 for overlooked Down syndrome genes
There’s no doubt that an extra copy of chromosome 21 is what causes Down syndrome. There’s a lot of doubt, however, over which particular gene—or combination of genes—on chromosome 21 is the actual cause of its symptoms. To flesh out our understanding, geneticists must grapple with this large chunk of the genome that includes more…
-
The fox and the cranium
Although foxes look cuddly, these wild animals are equipped with sharp bites—and temperaments to match. Fear not, however, if you’re dying to get close to theses fluffy foxes: a nearly 60-year-old experiment has produced a line of them that are friendly enough to pet. The process of creating these tame foxes mirrors the way…
-
Zooming in: population genetics on a mitochondrial level
The mitochondria powering your cells are not all genetically identical. Genetic variation across the mitochondria of a single individual is common. This diversity is called mitochondrial heteroplasmy, and it plays an important role in the severity of mitochondrial disease. Problematically, the complexities of mitochondrial inheritance makes it extremely difficult to predict how this diversity is…
-
From fish tank to bedside
Yeast and zebrafish are among the lab organisms being recruited to the search for rare disease cures. Rare diseases are not so rare. About 300 million people worldwide live with the more than 7000 individual diseases that are designated “rare” by the US government. But because each of these affect so few individuals, the usual…
-
Get outbred: Genetic diversity in laboratory gerbils
Biologists rely on animal models to answer important questions that can’t be addressed with cells in a dish. Often, these animals are deliberately inbred; a less diverse population of animals means that data obtained from experiments with these animals will be less noisy and easier to interpret, so fewer animals are needed for meaningful results.…
-
Behind the cover: Drosophila Halloween genes
Fruit fly mutants can sometimes be grisly. Ecdysteroid hormones control aspects of fly development, including molting and metamorphosis; because aberrations in these genes lead to embryos with a ghastly appearance, they have been collectively dubbed “Halloween genes.” In a study published in GENETICS, Uryu et al. investigated how the expression of these genes is regulated.…
-
Using CRISPR for tissue-specific gene knockouts in Xenopus
Why study human diseases in frogs? For starters, 79% of genes implicated in human disease have orthologs in the African clawed frog Xenopus laevis. Frogs also produce hundreds of embryos that can be grown in a dish, meaning they can be manipulated in ways that are impractical on a large scale in mammals. For example,…